True Course vs True Heading vs Magnetic (How Are They Different?)
When you plot your flight route on your sectional chart and begin to fly it, you might find that the aircraft veers off course after a while. You might begin to wonder why the aircraft doesn't follow the same exact path as you had thought it would. The reason for this is found in the True Course, True Heading and Magnetic Heading.
We will uncover the differences between them and their crucial roles in aviation. Let's unearth these mysteries together—read on to learn how they vary and why that matters for pilots.

Featured Pilot Gear
Browse our selection of high-quality pilot supplies! Your purchase directly supports our small business and helps us continue sharing valuable aviation content.
When you plot your flight route on your sectional chart and begin to fly it, you might find that the aircraft veers off course after a while. You might begin to wonder why the aircraft doesn't follow the same exact path as you had thought it would.
There's a captivating explanation for this phenomenon that aspiring pilots should know. True Course, True Heading, and Magnetic Heading are all essential navigational terms to recognize when it comes to aerial navigation.
We will uncover the differences between them and their crucial roles in aviation. Let's unearth these mysteries together—read on to learn how they vary and why that matters for pilots.
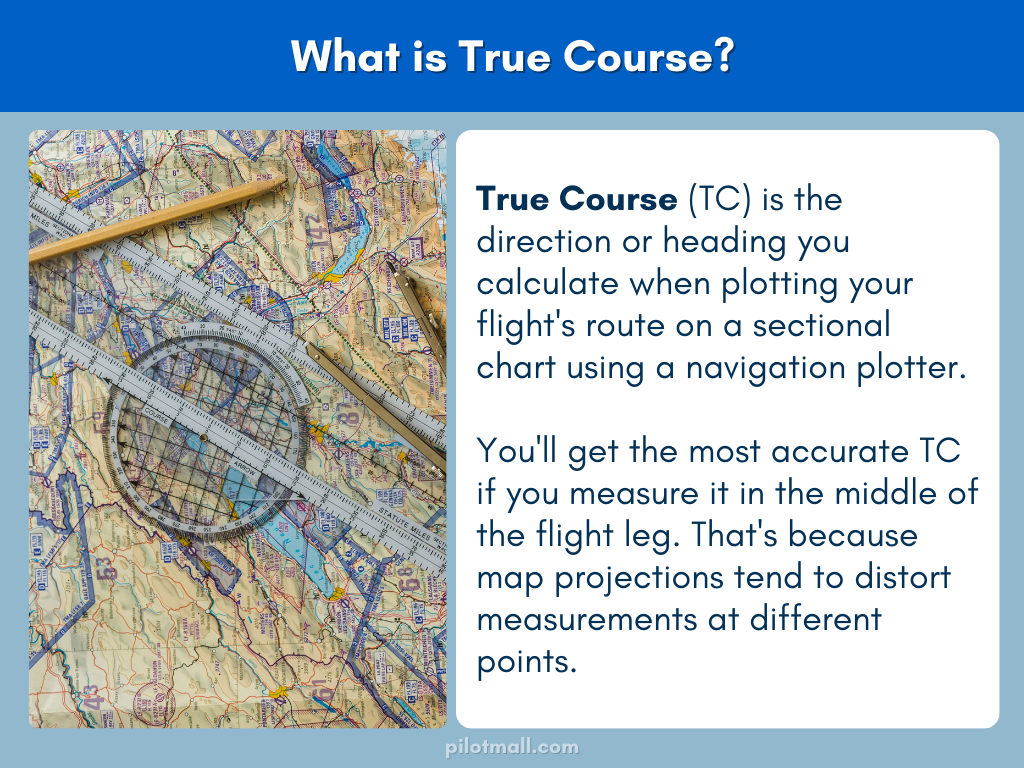
What is True Course?
True Course (TC) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. You'll get the most accurate TC if you measure it in the middle of the flight leg. That's because map projections tend to distort measurements at different points.

What is True Heading?
True Heading (TH) is the actual direction an aircraft points, corrected for magnetic variation and wind, and referenced to true north. You’ll need to adjust for the wind to determine your actual course.

What are the Differences?
While sharing similarities there are some key differences between all three types of directional headings.
True Course vs. True Heading
The true course is the desired directional route of flight and is usually the same as bearing if the route goes directly between two points.
True Heading vs. Magnetic Heading
The difference between a true heading and a magnetic heading is that the magnetic heading is the direction read off the magnetic compass, corrected by using the compass card. This will be different from the magnetic course due to winds aloft.
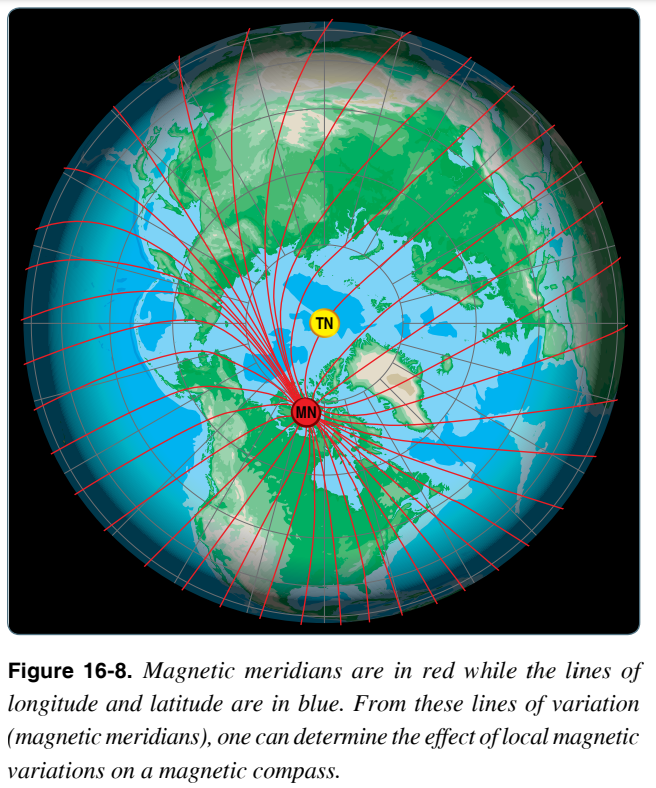
True North vs. Magnetic North
You might be wondering if true and magnetic north are the same, but the earth has two different North's. True both is the geographic north pole, while the other is the magnetic north pole. The north magnetic pole is located somewhere in the northern hemisphere around northern Canada.
To put it simply, due to the Earth's magnetic field, the compass north will lead to the magnetic north pole. The true north pole, or the celestial north pole, is the point on the Earth's surface that intersects the Earth's rotational axis.

How to Calculate Them
Calculating and understanding how true course, true heading, and magnetic heading work is vital for planning cross-country flights.
Materials needed:
- Pen or Pencil (Preferably pencils in case of mistakes)
- Notebook/Paper
- E6-B Flight Computer
- Navigational Plotter
- VFR Sectional Chart (preferably one for the area you intend to fly in)
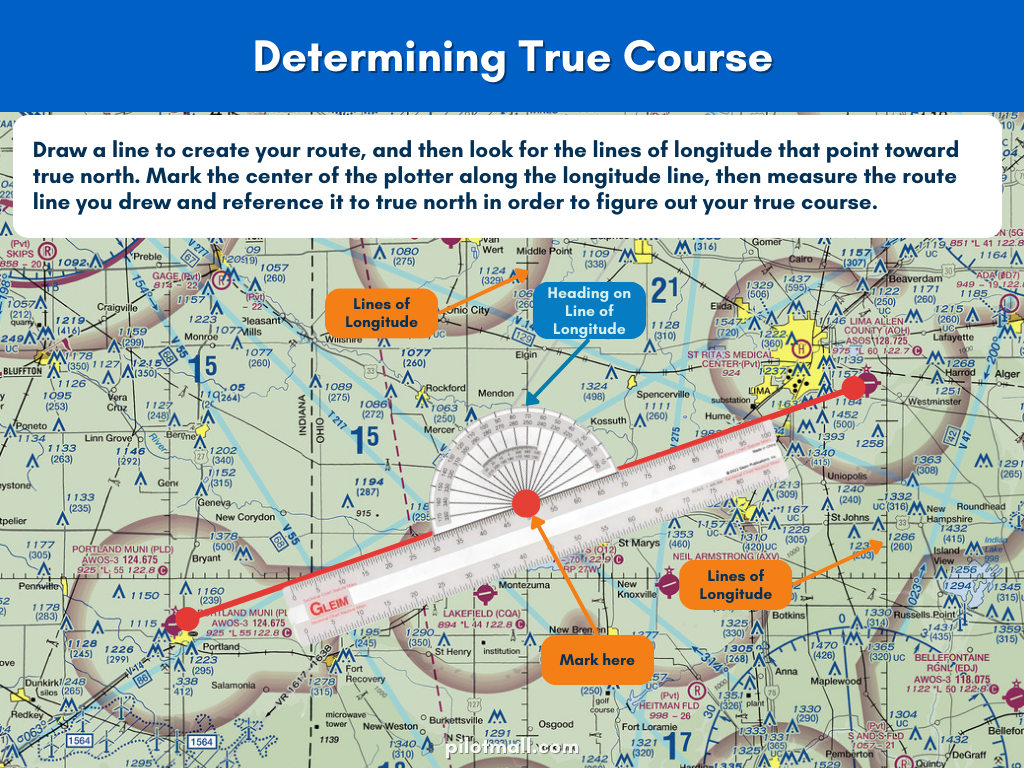
Calculate True Course
- Get out your plotter and your sectional chart. Draw a line to create your route, and then look for the lines of longitude that point toward true north.
- Mark the center of the plotter along the longitude line, then measure the route line you drew and reference it to true north in order to figure out your true course.
If your course is going from north to south and there is no line of longitude on your flight path you will have to use a line of latitude, which runs horizontally on the sectional.
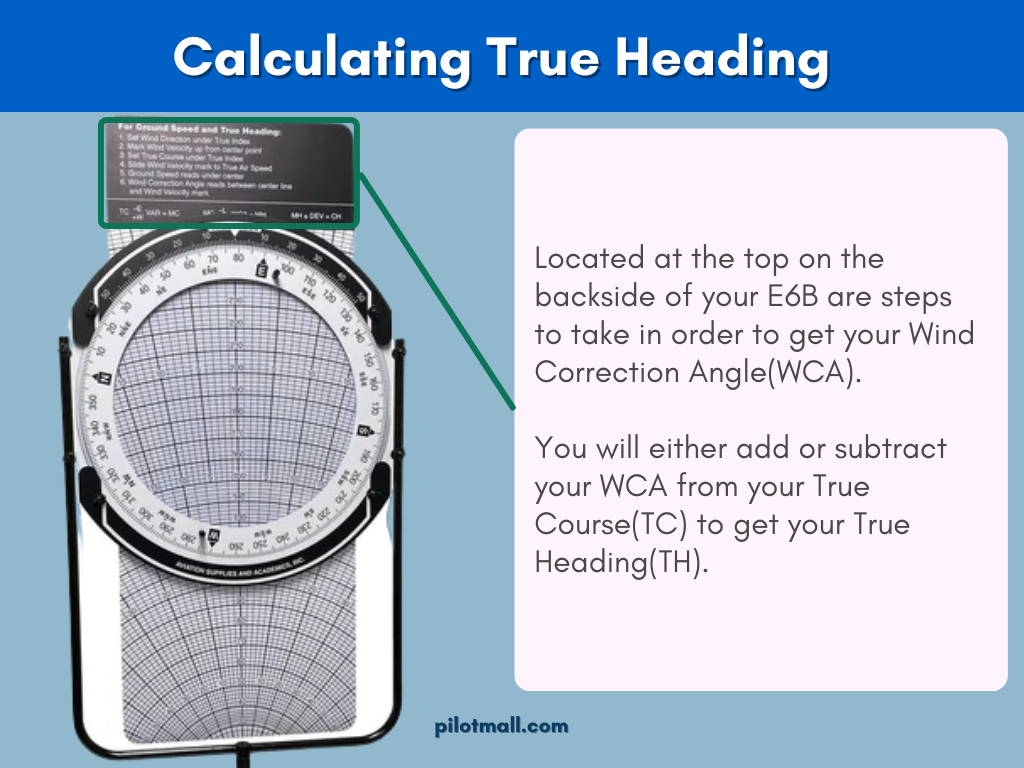
Calculate True Heading
To figure out your True Heading you will need to use a flight computer like an E6B or something similar to make corrections according to forecast winds aloft. Additionally, Forecast Winds and Temperature Aloft charts (FD) are based on true north as a reference point.
EXAMPLE: Let's say our True Course is 180°.
- To figure out your true heading you will take your true course and either add or subtract the drift angle from it.
- Get the direction, strength, and speed of the wind aloft. For this example, let's make our wind direction 215° and our wind speed 20kts.
- Get out your E6B and reset it by aligning the "N" symbol with the "True Index" and the center point with 100.
- Set the wind direction (I.E. 215°) under the "True Index."
- Using a pencil mark the wind velocity(I.E. 20) up from the center point, for this example that would be placing a dot on the 120 mark.
- Slide the wheel to set your True Course under the True Index, this should line up "S" with the True Index.
- Slide the rectangular wind velocity until the dot you marked lines up with the wind velocity mark(in this case line the dot up with the 120 line) to mark the true airspeed.
- Your Ground speed will read under the center of the wheel, which would be just around 100-101 GS in this example.
- The Wind Correction Angle will be counted from the centerline to the dot. For this example, the dot is about 3 boxes over to the right, so close to a 6° WCA.
- If the dot is on the right side of the centerline we add the WCA, if it's on the left, we subtract it from the True Course. (I.E. TC 180 + WCA 6 = TH 186)
- In our example, the True Heading would be 186 in order to maintain the aircraft on the 180 True Course.
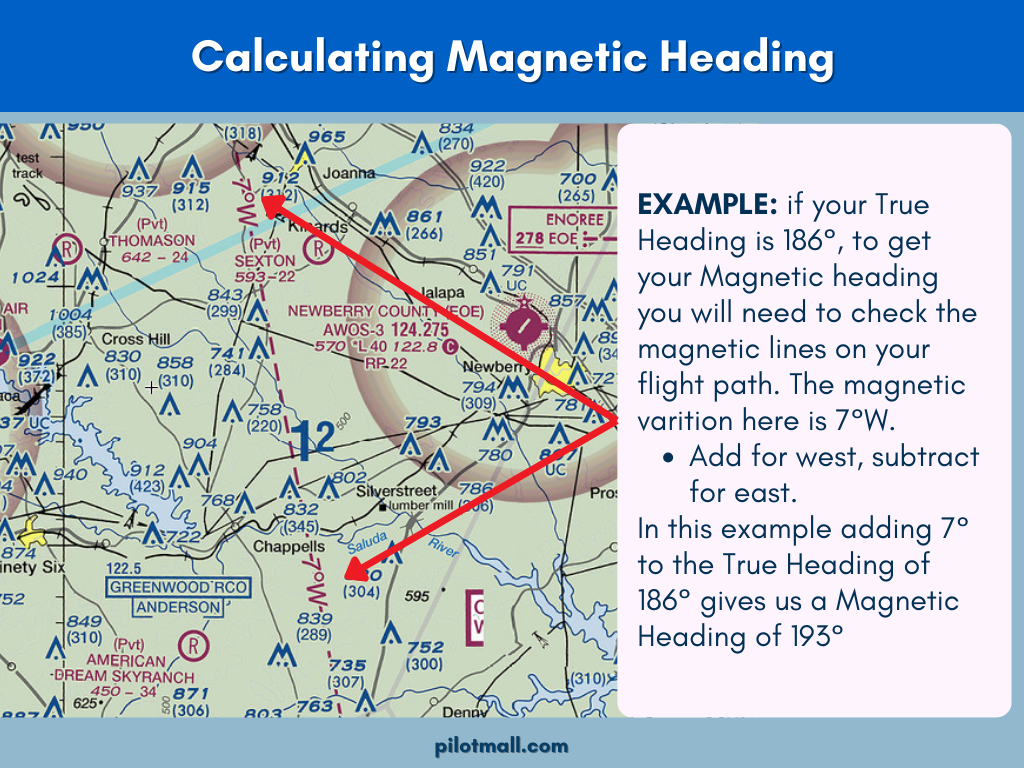
Calculate Magnetic Heading
Calculating magnetic heading involves taking into account the magnetic deviation, also known as magnetic variation, which arises from the Earth's magnetic poles not aligning perfectly with its geographic poles.
When using a magnetic compass, you'll notice that it points to magnetic north, which isn't necessarily the same as true north.
To obtain the correct magnetic heading, you'll need to apply the magnetic variation or declination specific to your location. This variation is given in degrees, and it can vary significantly depending on where you are on the planet.
EXAMPLE:
If we use a True Heading of 186° and along our intended flight path the magnetic lines show 7° W, then we will add 7 to our TH(add for west, subtract for east). This would make our MH 193° .
By adjusting your magnetic headings to compensate for this magnetic variation, you ensure that your compass guides you accurately, keeping you on the right course during your journeys.

Why They Matter
Knowing the difference between True North and Magnetic North is still extremely important when it comes to flight planning. Although advancements in GPS and digital technology have simplified things, pilots are still expected to know how to plot a course by relying on traditional navigation methods.
The distinction between the two is referred to as Magnetic Declination, which can be thought of as an offset between the True North reading from a map and the Magnetic North reading with a compass.
Whenever navigators use their compasses with maps, a correction must be applied to account for this difference.
Using a magnetic compass is one of the most reliable ways to navigate because it does not depend on electronics. Even if all your navigation systems or primary batteries fail, your compass can tell you where the magnetic pole is (which can differ slightly from the real pole depending on your location).

Frequently Asked Questions
- What is "Celestial North"?
- Wikipedia describes this as, "The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere."
- What is "Polaris"?
- Polaris is another name for the north star, it is a fairly bright star that shines in the night sky and is the brightest star near the Earth's rotational axis point. Explorers and navigators have used this star for navigational purposes for over 1,000 years.
- What is magnetic variation?
- Magnetic declination (or variation) is considered the angular difference between magnetic north and true north. They are displayed as dashed magenta lines on a sectional map.
- Magnetic vs. true heading - what's the difference?
- A true heading is the course corrected for magnetic variation, and a magnetic heading is the position read directly off your aircraft compass.
- What is true course vs. true heading vs. magnetic heading?
- A true course is a heading based on the direction you intend to travel. A true heading is the course corrected for magnetic declination, and a magnetic heading is the compass heading read directly off your aircraft compass.
- What does true heading mean?
- One corrected for magnetic variation, the true heading is the actual directional heading an aircraft is pointing.
- Do pilots use magnetic or true north?
- Pilots use both. They can apply variation to magnetic north if they have true north. In modern days, the Global Positioning System (GPS) has made navigating north much easier than in the past. True north is a fixed point on the top of the earth's axis. Magnetic north is a direction compass needle points to due to the earth's magnetic field.
- Should ATC headings be true or magnetic?
- ATC will provide you with a heading based on the direction they see the aircraft pointed in and moving towards. This means that ATC uses your ground track when giving headings.
 |
ASA Color E6BASA's Color E6B takes the standard "whiz wheel" manual flight computer and updates it with striking color accents. Though identical in functionality and size to its standard ASA-E6B, this version of the solid aluminum flight computer utilizes a variety of colors to signify its various functions. |
Takeaway
As we wrap up our journey through understanding magnetic north, the geographic north pole, and the art of calculating true course and true heading, I want to leave you with something personal and heartfelt.
For all you student pilots out there, remember that understanding these concepts might feel hard at first, but the more you read, learn, and love aviation, the more these processes will become second nature to you.
It's like when the explorers of times long past learned to read the stars in the night sky, adopting how to calculate these headings will not only help you navigate the air but draw you closer to reaching your goal as a career pilot.
As you embark on your flights, may you always find your way, guided the magnetic north. Fly safe, and let the skies be your canvas for a lifetime of adventures, both in the air and in the heart.
Did you enjoy learning about True Course vs True Heading?
Check out these links to learn more about aviation educational guides.
- 10 Types of Altitude Explained: A Guide for Pilots
- How to Read an Altimeter (Complete Guide)
- Maneuvering Speed: A Full Comprehensive Guide
- How it Works: Airspeed Indicator (Extensive Guide)
Did you find this article helpful?
Do you think we missed anything important? Let us know in the comments below!










3 comments
As a retired USAF nav, Ned is correct. This page needs to be fixed. “A true course is a heading based on the direction you intend to travel. A true heading is the course corrected for magnetic declination.” The second sentence is describing Mag Course. True heading is true course corrected for winds.
Thank you so much for this informative article. Amazing work and very helpful.
True Course (TC) is what you measure with your plotter off a sectional chart.
True Heading (TH) is your TC corrected for winds using your Whiz Wheel.
Mag Heading (MH) is your TH corrected for mag var and that is what you fly.
Reference: Air Force Manual 51-40, Air Navigation.
Navigators care about TC and TH etc. But, pilots want the MH to fly.