How to Read METAR Aviation Reports (Complete Guide)
One of the skills pilots must learn and excel at is meteorology. It is important to be adept at reading weather reports and forecasts then using them to make informed flight decisions. There are multiple reports to consult, and METARs are one of the primary sources for current weather information. Learning how to read a METAR is a key part of being a safe pilot.

Featured Pilot Gear
Browse our selection of high-quality pilot supplies! Your purchase directly supports our small business and helps us continue sharing valuable aviation content.
Whether you are a student pilot just starting out or an experienced aviator brushing up on your weather knowledge, this guide is designed to be your complete resource for aviation weather reports. We’ll walk through how to read METARs step by step, compare them with TAFs, explain PIREPs, AIRMETs, and SIGMETs, and show you how to use all of them together to make safer, smarter flight decisions. Use the table of contents below to jump to the section you need, or read it straight through to master the full picture of aviation weather.
Introduction: Why Weather Literacy Is a Pilot’s Most Important Skill
A student pilot, preparing for a cross-country flight, pulls up the weather briefing. The forecast looks marginal, with a TEMPO condition in the destination TAF calling for low ceilings. An hour later, a newly issued PIREP from a similar aircraft along the planned route reports moderate turbulence and icing precisely where the forecast showed only scattered clouds. Armed with this complete picture—the forecast of what might be and the pilot report of what is—the student makes the correct, safe, no-go decision.
This scenario is not academic; it’s the essence of airmanship. Weather literacy transcends memorizing codes. It’s the art and science of interpreting atmospheric data to make life-or-death decisions. This guide is designed to be the most comprehensive resource you need—moving far beyond METARs into TAFs, PIREPs, AIRMETs, and SIGMETs—and, most importantly, how to synthesize them into a single, cohesive mental model for sound aeronautical decision-making.
Aviation Weather at a Glance: METAR, TAF, PIREP, AIRMET & SIGMET
There are multiple reports to consult, and METARs are one of the primary sources for current weather information. Learning how to read a METAR is a key part of being a safe pilot. But the complete picture includes:
- METAR: Current conditions (observation).
- TAF: Forecast for the next 24–30 hours at an aerodrome.
- PIREPs: Real-time pilot observations aloft.
- AIRMET: Widespread areas of moderate hazards (IFR/mountain obscuration, turbulence, icing).
- SIGMET & Convective SIGMET: Severe/non-convective and convective hazards hazardous to all aircraft.
The true mark of expertise is not decoding these in isolation, but synthesizing them to make better decisions.
Where to Get Official METARs & TAFs
For an official weather source in the United States, use the Aviation Weather Center. At the top of the page, go to “Products” → “METAR Data.” Apps and services such as ForeFlight can also provide accurate weather information and factor it into your flight plan.
The Aviation Weather Center has recently (as of October 2023) updated its website with a cleaner, more mobile-friendly interface. We’ll help you navigate these changes throughout this guide.
METAR vs. TAF (Quick Comparison)
Before decoding, understand the core difference: METARs tell you what is happening now; TAFs tell you what is likely to happen later. Pilots plan with TAFs and verify with METARs before departure.
| Feature | METAR (Observation) | TAF (Forecast) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | “What is the weather right now?” | “What will the weather be like later?” |
| Validity | Valid for 1 hour (until next report) | Valid 24–30 hours |
| Issuance | Typically ~55 minutes past the hour | Every 6 hours (4× daily) |
| Use Case | Immediate conditions, arrival checks | Go/no-go planning, alternates |
Mastering the METAR: 11 Parts, Codes & Examples
What are METARs?
A METAR, also known as a Meteorological Aerodrome Report or Meteorological Terminal Aviation Routine Weather Report, is a concise report on the current weather conditions at a given location. METARs are issued hourly just before the top of the hour by the Aviation Weather Center. They are valid for 1 hour after issuance.
Pilots can access METARs through the NOAA National Weather Service Aviation Weather Center or via EFB apps (ForeFlight, etc.). For the most robust picture, consult both METARs and TAFs.
2 Types of METARs
The standard hourly report is simply called a METAR. If dangerous conditions emerge between routine reports, an unscheduled SPECI (special) is issued. A SPECI is a red flag that conditions are changing quickly.
How to Read a METAR Report (11 Parts)
A METAR contains valuable information condensed into blocks of coded data separated by spaces.
1. Type of Report
METAR (routine) or SPECI (special). SPECI indicates a significant, often rapid change since the last METAR.

2. Station Identifier
Four-letter ICAO code. In the contiguous U.S., station identifiers start with “K” (e.g., KLAX). Alaska and Hawaii begin with “PA” and “PH”; Canada uses “C-” prefixes; Mexico uses “MM”.

3. Date and Time
Six digits plus “Z” (Zulu/UTC). First two digits = day of month; next four = time (HHMM). Routine METARs typically appear near :55 past the hour.

4. Modifier
AUTO (fully automated) or COR (corrected). No modifier generally means a human observer or supervised automation.
5. Wind Information
Direction (true) in degrees + speed in knots, e.g., 19004G10KT (from 190° at 4 kt, gusting 10). VRB indicates variable direction.

6. Visibility
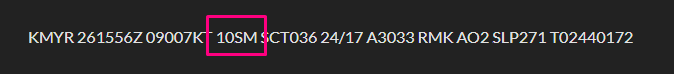
Prevailing visibility in statute miles (e.g., 10SM). Fractions are common (e.g., 1/2SM). M means “less than” (e.g., M1/4SM). Large airports may include RVR (runway visual range).
7. Present Weather
Three-part code: intensity (+ heavy, - light, none = moderate), descriptor (e.g., SH showers, TS thunderstorm, FZ freezing), and phenomenon (e.g., RA rain, SN snow, FG fog, BR mist, HZ haze).
| Code | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| RA | Rain | +RA (Heavy Rain) |
| SN | Snow | -SN (Light Snow) |
| DZ | Drizzle | FZDZ (Freezing Drizzle) |
| GR | Hail | TSGR (Thunderstorm with Hail) |
| PL | Ice Pellets | PL (Moderate Ice Pellets) |
| FG | Fog | FG (< 5/8 SM) |
| BR | Mist | BR (≥ 5/8 SM) |
| HZ | Haze | HZ |
| TS | Thunderstorm | VCTS (TS in the vicinity) |
8. Sky Condition
Reported lowest to highest: coverage (FEW/SCT/BKN/OVC) plus base in hundreds of feet AGL (e.g., SCT028 = scattered at 2,800’). Ceiling is the lowest BKN/OVC layer. Special tags may appear (e.g., CB cumulonimbus, TCU towering cumulus, VV vertical visibility).

| Code | Sky Coverage (Oktas) | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| SKC | 0/8 | Sky clear (manual) |
| CLR | 0/8 | Clear (automated, below 12,000’) |
| FEW | 1/8–2/8 | Few |
| SCT | 3/8–4/8 | Scattered |
| BKN | 5/8–7/8 | Broken (ceiling) |
| OVC | 8/8 | Overcast (ceiling) |
9. Temperature and Dew Point
TT/DD in °C (e.g., 18/02). A leading M indicates minus temperatures (e.g., M05).

10. Altimeter and Pressure
A#### in inches of mercury (e.g., A2990 = 29.90"). Outside the U.S., Q#### in hPa (e.g., Q1013).

11. Remarks (RMK)
Additional details often overlooked by beginners: station type (e.g., AO2 has a precipitation discriminator), sea-level pressure (SLP), exact temperatures (T group), pressure trends (PRESFR/PRESRR), lightning, hail sizes, virga, and more.

Example: KLAX METAR (Fully Decoded)
METAR KLAX 180845Z 19004G10KT 10SM -SHRA FEW018 SCT028 OVC040 18/02 A2990 RMK AO2 SLP121 T01820021
- METAR: Routine hourly observation.
- KLAX: Los Angeles International.
- 180845Z: On the 18th at 08:45Z.
- 19004G10KT: Wind from 190° at 4 kt, gusting to 10 kt.
- 10SM: 10 statute miles visibility.
- -SHRA: Light rain showers.
- FEW018 SCT028 OVC040: Few 1,800’; scattered 2,800’; overcast 4,000’ (ceiling 4,000’).
- 18/02: Temp 18°C, Dewpoint 2°C.
- A2990: Altimeter 29.90”.
- RMK AO2 SLP121 T01820021: AO2 station, sea-level pressure 1012.1 hPa, precise temp/dewpoint 18.2°C/2.1°C.
Practice with a Simpler Sample METAR
METAR KLAL 151250Z 11004KT 10SM SCT030 26/24 A3004
- KLAL: Lakeland Linder International (K = U.S.).
- 151250Z: 15th at 12:50Z.
- 11004KT: Winds 110° at 4 kt.
- 10SM: 10 statute miles.
- SCT030: Scattered 3,000’.
- 26/24: Temp 26°C / Dewpoint 24°C.
- A3004: Altimeter 30.04”.
- RMK: None.
Want to test your decoding on a gnarly one? Try this excellent challenge:
Watch the METAR to decode, then check your work against the answer video.
Reading a TAF Like a Pro (TEMPO, FM, BECMG, PROB30/40)
TAFs predict terminal area weather for 24–30 hours. They use change groups to indicate how conditions evolve:
- TEMPO: Temporary fluctuations (generally < 1 hour at a time; < half the period total).
- FM: “From”—rapid, significant change to new prevailing conditions after the FM time.
- BECMG: “Becoming”—gradual change over a window; new state fully in place by the end time.
- PROB30/40: 30%/40% chance of specified phenomena during a time window (often TS/precip).
Example TAF (KORD): Step-by-Step
TAF KORD 051130Z 0512/0612 14008KT 5SM BR BKN030 TEMPO 0513/0516 1SM -RA FG OVC008 FM051600 16010KT P6SM SCT040 BECMG 0520/0522 24015G25KT P6SM SCT015 BKN025 PROB30 0602/0606 2SM TSRA OVC010CB
- Baseline: 140@8 kt, 5SM in mist, BKN030.
- TEMPO 13–16Z: Periods of 1SM -RA FG, OVC008 (IFR; plan alternates).
- FM 16Z: Decisive improvement to VFR (P6SM, SCT040).
- BECMG 20–22Z: Gradual trend to gusty 24015G25, lower layers (SCT015 BKN025).
- PROB30 02–06Z: 30% chance of 2SM TSRA OVC010CB (very conservative planning advised).
PIREPs: Real-Time Weather From the Cockpit
PIREPs (UA) are pilot observations; UUA denotes urgent conditions (e.g., severe turbulence/icing, tornadoes). Always check two key contexts: time (freshness) and aircraft type (a “light chop” in a heavy jet can be “moderate” in a light single).
Example PIREP (decoded)
KCMH UA /OV APE 230010/TM 1516/FL085/TP C172/SK BKN040-TOP080/TB LGT/IC TRACE
- Over APE VOR, 10 NM on 230 radial; 15:16Z; 8,500’; C172; BKN040 tops 8,000; light turbulence; trace icing.
AIRMETs & SIGMETs: Area Advisories & Severe Warnings
AIRMET (WA)
- Sierra: IFR and/or extensive mountain obscuration (“Sierra for See”).
- Tango: Moderate turbulence, surface winds ≥ 30 kt, non-convective LLWS.
- Zulu: Moderate icing; freezing level info (“Zulu for Zero”).
Remember: An AIRMET outlines a large area; hazards may be localized within it. Use PIREPs/METARs to pinpoint.
SIGMET (WS) & Convective SIGMET (WST)
- SIGMET: Severe icing (non-TS), severe/extreme turbulence or CAT (non-TS), widespread dust/sand < 3SM, volcanic ash (valid up to 4 hours; unscheduled).
- Convective SIGMET: Severe thunderstorms—lines, embedded, large areas; tornadoes; hail ≥ 3/4”; surface gusts ≥ 50 kt (issued hourly at :55; valid 2 hours). Treat the entire area with wide avoidance.
From Data to Decision: Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1: Pre-Flight Go/No-Go
Route: KDEN → KMCI (VFR). TAF KMCI shows BECMG 2022 2SM -TSRA BKN020CB (deterioration near arrival). AIRMETs for turbulence/IFR over eastern KS. METARs trending pressure falls west of KMCI. PIREPs lacking from light aircraft. Decision: No-Go.
Scenario 2: In-Flight Diversion
Route: KPHX → KABQ at 11,500’. New Convective SIGMET for a developing embedded line ahead; UUA PIREP reports SEV TURB at higher altitudes. Action: 180° turn, coordinate diversion with ATC (e.g., KFLG). Live-saving, textbook ADM.
Quick-Reference: Hazard Identification & Pilot Actions
| Weather Code/Phenomenon | Found In | Associated Dangers | Recommended Pilot Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thunderstorms (TS, CB) | METAR, TAF, SIGMET | Severe turbulence/icing, hail, lightning, wind shear | Avoid by ≥ 20 NM; do not fly over/under; circumnavigate or divert. |
| Freezing Rain (FZRA) | METAR, TAF, PIREP | Severe structural icing; rapid accumulation | Avoid at all costs; change route/altitude; delay. |
| LIFR (Low IFR) | METAR, TAF, AIRMET | CFIT risk; disorientation | No VFR flight; IFR only if proficient, current, equipped. |
| Severe Turbulence (SEV TURB) | PIREPs, SIGMET | Loss of control; structural risk | Slow to Va; exit area immediately; avoid SIGMET polygons. |
| Moderate Icing (MOD ICE) | PIREPs, AIRMET Zulu | Performance loss; control issues | Activate anti-/de-ice; change altitude/course; exit promptly. |
| Mountain Obscuration | AIRMET Sierra | Terrain/CFIT | Avoid VFR through terrain; use clear passes only. |
Essential Tools & Resources for Modern Pilots
- Official Source: AviationWeather.gov (Aviation Weather Center). Use Graphical Forecasts for Aviation (GFA) and product layers for METARs, TAFs, PIREPs, AIRMETs, and SIGMETs.
- EFB Apps: ForeFlight, Garmin Pilot, etc. Decode and overlay products on your route.
- Practice: Use interactive quizzes and video walk-throughs (e.g., the MzeroA decoding videos above) to build speed and accuracy.
- Infographics: Visual breakdowns of METAR/TAF formats reinforce sequence and meaning of each element.
Aviation Weather FAQ
What’s the main difference between a METAR and a TAF?
METAR = observation of current conditions (valid about an hour). TAF = forecast of future conditions (valid 24–30 hours).
What does RMK AO2 mean in a METAR?
Automated station with a precipitation discriminator (can tell rain vs. snow).
What’s the difference between SKC and CLR?
Both mean sky clear; SKC is manual, CLR is automated (no clouds detected below 12,000’).
How old is too old for a PIREP?
Depends on the phenomenon. For fast-moving hazards like TS location, 15–20 minutes can be “stale.” Stable cloud layers can remain useful longer.
Why do some codes look odd, like FU for smoke?
Many abbreviations have French roots: FU (fumée), BR (brume), GR (grêle).
What does BECMG mean in a TAF?
A gradual change expected during a time window; by the end of the window, the new state is fully established.
Is it safe to fly in an area covered by an AIRMET?
It flags potential moderate hazards over a broad area. Use PIREPs and nearby METARs to pinpoint the actual risk and plan deviations accordingly.
Should a pilot ever fly into an area covered by a SIGMET?
No. SIGMETs denote hazards to all aircraft. Convective SIGMETs, in particular, warrant wide avoidance.
Where’s the best place to get official aviation weather?
AviationWeather.gov (Aviation Weather Center). Supplement with your EFB.
Takeaways & Further Learning
METARs and TAFs are the foundation. PIREPs, AIRMETs, and SIGMETs complete the picture. The expert pilot reads all of them together and makes proactive, conservative decisions when risk creeps in.
Enjoyed learning about METARs?
Check out more guides to understand aviation weather:
- AWOS vs ASOS: What You Should Know
- How to Read a TAF (Terminal Aerodrome Forecast)
- Types of AIRMETs: Complete Guide on These 3 Conditions
- 12 Types of Clouds Pilots Must Recognize [#12 Can be Deadly]
Did you find this article helpful?
Do you think we missed anything important? Let us know in the comments below!